HTTP Endpoint
At CrateDB, we believe in breaking down barriers (technical, temporal and procedural) so your business can harness the full potential of its data. With CrateDB’s real-time analytics engine, you can act with speed and precision. One of the most direct and flexible ways to interact is via the HTTP endpoint: a simple, powerful REST-style interface for SQL.
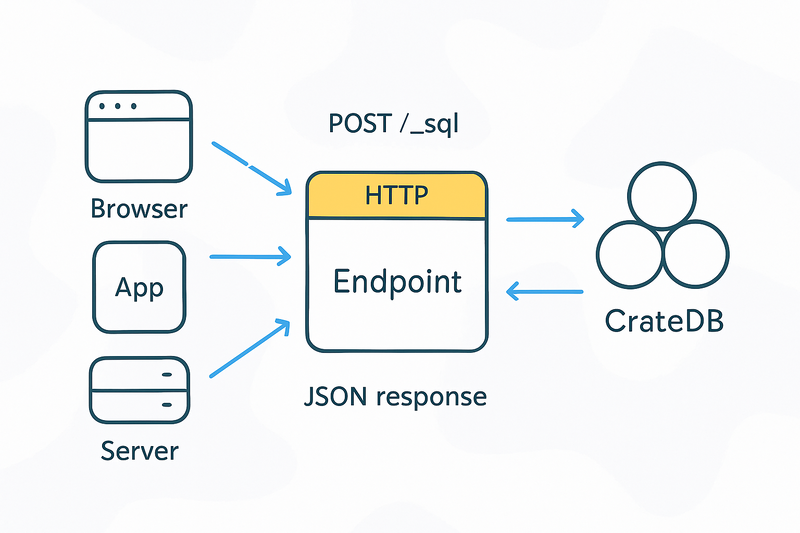
Why use the HTTP endpoint?
- Universal access: No specialized drivers needed, any tool or language that can make HTTP calls can speak to CrateDB.
- Simplicity with power: Submit full SQL queries (analytics, search, aggregations, joins) via HTTP in JSON format.
- Fluid integration: Ideal for embedding in microservices, server-less functions, automation scripts, event pipelines and real-time dashboards.
- Versatility: Works alongside PostgreSQL wire protocol and other native clients; you choose the best interface for your use-case.

Quick example in Curl
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"stmt": "SELECT name, age FROM users WHERE age > 30 LIMIT 5"}'

Getting started
- Endpoint URL
- By default, the HTTP endpoint is available at: http://<servername>:<port>/_sql
(for example http://localhost:4200/_sql)
- By default, the HTTP endpoint is available at: http://<servername>:<port>/_sql
- Request method & headers
- Use HTTP POST.
- Set Content-Type: application/json
- Request body format
The body should be JSON. At minimum you specify the "stmt" key with your SQL statement. Example:
{
"stmt": "SELECT user_id, count(*) AS c FROM events GROUP BY user_id ORDER BY c DESC LIMIT 10"
}
Additional parameters (such as bulk_size, page_size, params) may also be supported. - Response
CrateDB returns a JSON response, which includes metadata and the rows. Example structure:
{
"cols": ["user_id", "c"],
"rows": [
[123, 456],
[456, 123]
],
"rowcount": 2
}
(actual fields may vary, refer to the documentation) - Error handling
- If your SQL is invalid or the request fails, you’ll receive error details in the JSON response. Use standard HTTP error codes (4xx/5xx) as appropriate.

Use-cases & patterns
- Interactive analytics dashboards: Use HTTP to push queries, fetch results, and refresh visualisations in real time.
- Microservices & functions: A small service can call the HTTP endpoint directly to fetch or write data without a dedicated driver.
- Data ingestion & ad-hoc queries: Write rows (via INSERT or COPY), update data or run complex aggregations via the same endpoint.
- Automation & workflows: Trigger SQL via HTTP in CI/CD, monitoring scripts or operational pipelines (e.g., cleanup, archival, metrics).

Best practices
-
Use parametrised queries where supported (to avoid SQL injection).
-
Optimize your statements: while the HTTP interface is flexible, you still benefit from CrateDB’s strengths in distributed storage, indexing and real-time aggregation.
-
Manage timeouts & pagination: For large result sets, consider using pagination or streaming where supported.
-
Secure the endpoint: Use HTTPS, authentication (API tokens or other credentials) and role-based access control (especially in cloud or multi-tenant setups).
-
Monitor and tune: Track query performance, resource usage and response latencies. CrateDB’s real-time analytics and system tables provide visibility.

When to choose HTTP vs other interfaces
-
Choose HTTP when you want language-agnostic, lightweight access (e.g., REST, scripts, lightweight clients).
-
Use the PostgreSQL-wire interface (or one of the native client drivers) when you require full driver support, connection pooling or advanced driver-features.
-
For management and administrative automation in the cloud version, you may also use the CrateDB Cloud REST API (for clusters, users, roles, billing etc).

CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.