Distributed Query Engine
At the core of CrateDB lies its distributed SQL query engine, designed to handle massive data volumes, high ingestion rates, and complex queries across structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
It brings together the familiarity of SQL with the power of a distributed architecture, delivering millisecond-level insights even as your workloads grow exponentially.
What makes it distributed
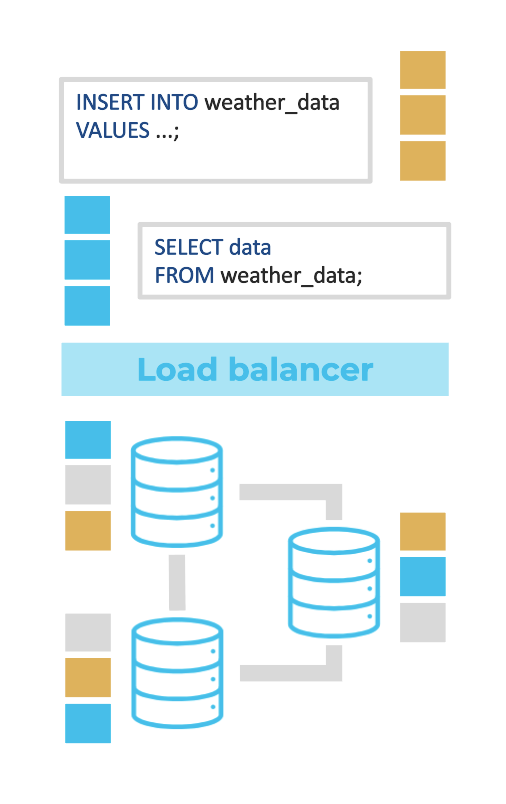
CrateDB automatically distributes data and queries across all nodes in a cluster.
Each node stores a subset of the data, executes part of the query, and returns intermediate results that are merged and optimized by the handler node (the node the client issuing the query is connected).
The result?
- Massive parallelization for faster query execution.
- Linear scalability as you add nodes.
- Built-in fault tolerance, no single point of failure.
You get real-time analytics at any scale, without tuning or manual sharding.

Why it matters
Traditional SQL databases struggle when data grows, especially with time series, logs, or IoT streams. CrateDB’s distributed SQL engine solves that by combining horizontal scalability, columnar performance, and automatic indexing.
- Ingest millions of records per second.
- Query across terabytes of data in milliseconds.
- Adapt instantly to changing analytics and AI needs.
Whether you’re analyzing industrial sensors, operational metrics, or application logs, CrateDB keeps performance predictable and queries simple.

How distributed execution works
- Data partitioning: Data is automatically sharded and replicated across nodes for parallel processing and resilience.
- Query distribution: When you run a query, the planner splits it into tasks and sends them to the nodes that hold the relevant data.
- Parallel execution: Each node performs its part (filtering, aggregating, joining, or searching) in parallel.
- Result merging: The handler node gathers and merges results, applying final sorts or aggregations before returning the answer.
This architecture ensures near-constant query times even as data volume scales up by orders of magnitude.

Built for real-time performance
CrateDB’s distributed engine isn’t just about scale, it’s about speed with intelligence:
- Columnar storage for efficient aggregation and analytics.
- Automatic indexing for instant access to new data.
- Adaptive query planner that optimizes joins, filters, and parallelism on the fly.
The outcome: Real-time queries that stay fast, even when your datasets reach billions of rows.

Query anything, anywhere
CrateDB’s distributed SQL engine works across multi-model data:
- Time series: Monitor operational metrics and KPIs continuously.
- Text: Run full-text search with MATCH.
- Vectors: Perform similarity queries using KNN_MATCH.
- Geospatial: Analyze location data with spatial functions.
- JSON: Query and filter nested objects using SQL dot notation.
All data types live together in the same cluster, and can be joined, aggregated, and analyzed using one unified SQL engine.

Resilience by design
CrateDB’s distributed SQL layer is built for continuous availability:
- Automatic data replication to protect against node failures.
- Dynamic rebalancing as nodes join or leave.
- Cluster-wide fault tolerance: queries reroute automatically when hardware fails.
- Zero downtime scaling: add or remove nodes on the fly.
You get the reliability of enterprise-grade infrastructure without operational complexity.

Transaction consistency with MVCC
CrateDB uses Multiversion Concurrency Control (MVCC) to manage transactions efficiently in a distributed environment.
This mechanism ensures that reads never block writes (and writes never block reads) by maintaining multiple versions of data in memory and on disk.
- Consistent snapshots: Queries always see a stable view of the data, even during concurrent updates.
- Non-blocking operations: High read/write concurrency without table-level locks.
- Distributed correctness: MVCC integrates with CrateDB’s query planner and replication logic to ensure global consistency across nodes and shards.

Example: query across billions of records
CrateDB’s distributed engine executes this query across all nodes in parallel, returning aggregated results in milliseconds, no matter the data volume.
SELECT region, COUNT(*) AS total_events, AVG(latency_ms) AS avg_latency FROM iot_telemetry WHERE ts > now() - INTERVAL '10 minutes' GROUP BY region ORDER BY avg_latency ASC;
CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.