Automatic Indexing
CrateDB automatically indexes every piece of data as it’s ingested, ensuring your queries stay fast, even as your datasets grow by billions of records. There’s no need to define indexes manually, manage schema changes, or tune performance. With automatic indexing, CrateDB combines the simplicity of SQL with the speed of modern search and analytics, giving you real-time results without operational overhead.
Why automatic indexing matters
When ingesting data, it’s not always clear which queries you’ll need in the future.
Use cases evolve, new business requirements emerge, and query patterns change over time.
CrateDB removes the complexity of anticipating index strategies. By automatically indexing every attribute by default, it ensures fast query responses for any query type, even when your data and workloads evolve.
- Instantly searchable data: New records are indexed within seconds of ingestion.
- Zero manual configuration: Indexing happens automatically, with smart defaults for every data type.
- Real-time analytics: Query freshly ingested data without delay.
- Operational simplicity: No DBA maintenance or reindexing required.

How automatic indexing works
CrateDB’s indexing subsystem is built on top of the Lucene search engine, deeply integrated into its distributed SQL architecture.
As data is inserted or updated:
- CrateDB automatically indexes each field, including nested JSON, text, vectors, and geospatial data.
- Indexes are distributed across nodes and shards for parallel query execution.
- Queries use these indexes transparently, combining search, filtering, and aggregation logic in one SQL operation.
This design delivers the best of both worlds, the expressiveness of SQL and the performance of a search engine.
CrateDB applies specialized indexing techniques tailored to each data type, ensuring optimal performance and flexibility across all workloads:
- Inverted indexes for text values
- Block K-D Trees (BKD) for numeric, date, and geospatial values
- HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) graphs for vector data

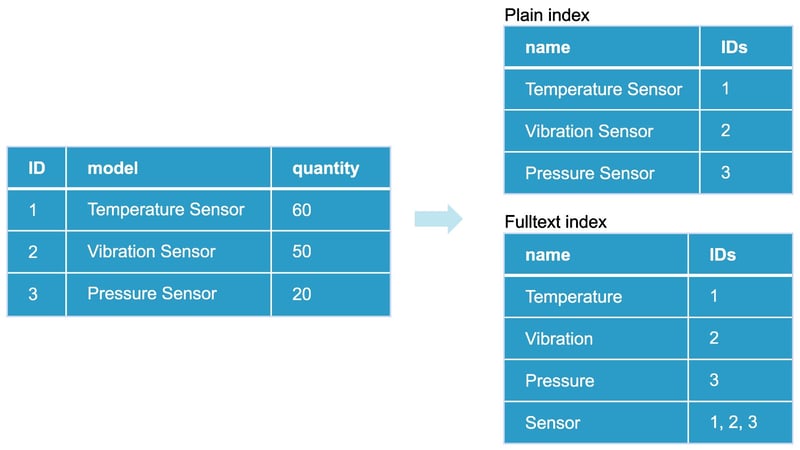
Inverted indexes for text values
Used for efficient search and filtering on text columns, enabling fast matches, wildcards, and regular expressions.
- Text columns use a plain inverted index by default (no text analysis).
- You can define full-text indexes with custom analyzers for advanced linguistic search.
CrateDB supports:
- 30+ languages, 11 analyzers, 15 tokenizers, and 35+ token filters,
- Plus full customization for analyzers and tokenizers, enabling features like fuzzy search, phrase queries, and attribute boosting.

Block K-D Trees (BKD) for numeric, date, and geospatial values
Highly efficient, IO-optimized indexes for structured and location-based data.
- Numeric values (including geopoints) are indexed using BKD-trees, which combine on-disk block structures with a lightweight in-memory binary tree for quick block lookups.
- This hybrid design delivers excellent query and update performance, even after millions of updates or large data movements.

HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) graphs for vector data
This enables fast similarity search using SQL’s KNN_MATCH() — ideal for embeddings, recommendations, and hybrid vector/text search.

Built for every data model
CrateDB indexes all supported data types automatically — from structured tables to complex objects:
| Data type | Indexing benefit |
|---|---|
| Relational | Fast lookups and aggregations on standard SQL tables |
| Time-series | Automatic time-based indexing for efficient rollups and trend analysis |
| JSON / Object | Each nested key-value pair indexed individually for flexible, ad-hoc queries |
| Full-text | Rich search capabilities with analyzers, scoring, and tokenization |
| Geospatial | Spatial queries using within(), distance(), and intersects() |
| Vector | Efficient approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) queries via KNN_MATCH() |
With CrateDB, any data you ingest is immediately queryable — regardless of format or structure.

Real-time queries on fresh data
CrateDB’s real-time ingestion pipeline and automatic indexing work hand in hand.
As soon as new events, logs, or sensor readings are written, they’re available for
- Aggregations
- Search queries
- Vector similarity
- Geospatial filters
- JOINs across multiple data sources

Advantages of automatic indexing
| Challenge | CrateDB solution |
|---|---|
| Manual index design | Fully automated, adaptive indexing |
| Delayed query access to new data | Real-time indexing on ingest |
| Performance degradation at scale | Distributed indexing across all nodes |
| Complex schema evolution | Dynamic field handling and nested object indexing |
| Separate search infrastructure | Integrated Lucene-based engine inside the database |
Automatic indexing turns CrateDB into a truly operational database, equally suited for analytics, search, and AI workloads.

Example: query instantly after ingest
// obj JSON { "MachineID" : "drill001", "Sensors" : [ { "name" : "temp1", "value": 21.5 }, { "name" : "temp2", "value": 20.8 }, { "name" : "accel", "value": 3.2 } ], "Events" : { "type" : "info"} }
// find all Machines that emit an INFO event and provide a temperature value SELECT obj['MachineID'] as "machine" FROM my_devices WHERE obj['Events']['type'] = 'info' AND 'temp1' = ANY(obj['Sensors']['name']);
CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.