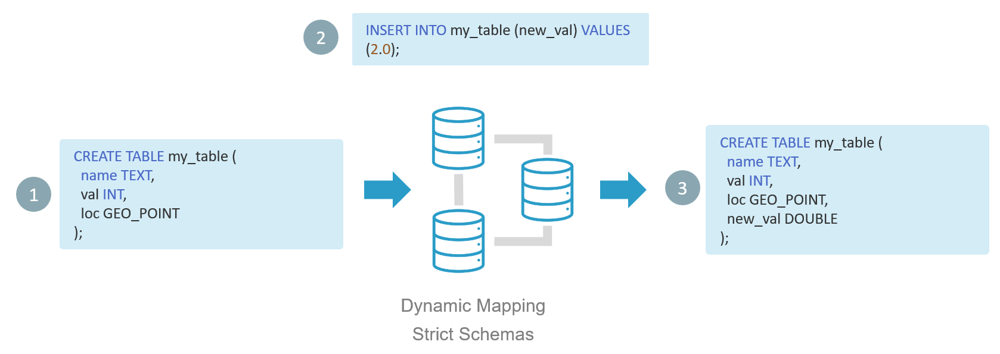
Dynamic Schemas
As your applications and data evolve, CrateDB’s schema evolves with them.
New fields, attributes, and data structures can be added automatically, without downtime or migrations, so you can keep ingesting and analyzing data in real time.
Why dynamic schemas matter
Data today is never static. IoT devices, modern apps, and analytics pipelines constantly introduce new fields, payload formats, or event types. In rigid databases, this means complex migrations, downtime, or inconsistent analytics.
CrateDB eliminates that complexity. Its dynamic schema capability allows your database to adapt instantly as new data arrives, while maintaining full SQL compatibility and consistency.
-
Automatic adaptation: New fields are added on the fly during ingestion.
-
No downtime: Schema changes happen transparently, without blocking queries or writes.
-
Fully indexed: Each new attribute is automatically indexed for real-time queries.
-
SQL simplicity: Use standard SQL to query both structured and semi-structured data.
CrateDB gives you the best of both worlds: the agility of NoSQL and the control of SQL.

How it works
When new data arrives, CrateDB detects unseen fields and adapts the schema dynamically, all while keeping operations online.
- The database receives a record with a new column or nested field.
- The dynamic schema engine infers the data type from the value.
- The schema is automatically updated to include the new field.
- The data is immediately indexed and available for queries.
You can configure schema flexibility per table using the dynamic parameter:
- dynamic = true → Automatically adds new fields as they appear (default).
- dynamic = false → Ignores unknown fields for strict schema control.
- dynamic = strict → Rejects unknown fields to enforce full structure.
This lets teams choose the right balance between flexibility and governance.

SQL–NoSQL flexibility in one engine
CrateDB’s hybrid architecture blends relational and document-style storage seamlessly:
- Relational records stored as JSON documents can change structure on the fly, simplifying the storage and analysis of complex, evolving data.
- JSON objects can be stored in OBJECT columns, which support arbitrary numbers of attributes, nested levels, and even arrays of objects.
- Schemas can still be enforced with configurable behavior: choose whether CrateDB should throw an error or automatically update the schema when encountering new fields.

Dynamic schema evolution in CrateDB Cloud
CrateDB Cloud extends this capability with schema evolution support during bulk uploads.
When uploading multiple files with differing schemas:
- CrateDB automatically updates the target table schema to accommodate new columns.
- You can enable or disable this behavior based on your data governance policy.

Why teams choose CrateDB
- Zero downtime: schema evolution happens online and transparently.
- SQL across everything: one language for structured and semi-structured data.
- Automatic indexing: every new field is instantly indexed.
- Cloud-ready flexibility: schema evolution options for bulk uploads and ingestion workflows.

Example: evolving data, no migration required
CREATE TABLE events ( device_id TEXT, timestamp TIMESTAMP, properties OBJECT(DYNAMIC) ); INSERT INTO events (device_id, timestamp, properties) VALUES ('sensor-01', now(), { "temp": 22.5, "humidity": 60 }); -- Later, a new field appears INSERT INTO events (device_id, timestamp, properties) VALUES ('sensor-01', now(), { "temp": 23.1, "humidity": 58, "pressure": 1015 }); -- The 'pressure' field is automatically added, typed, and indexed SELECT AVG(properties['pressure']) FROM events;
CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.