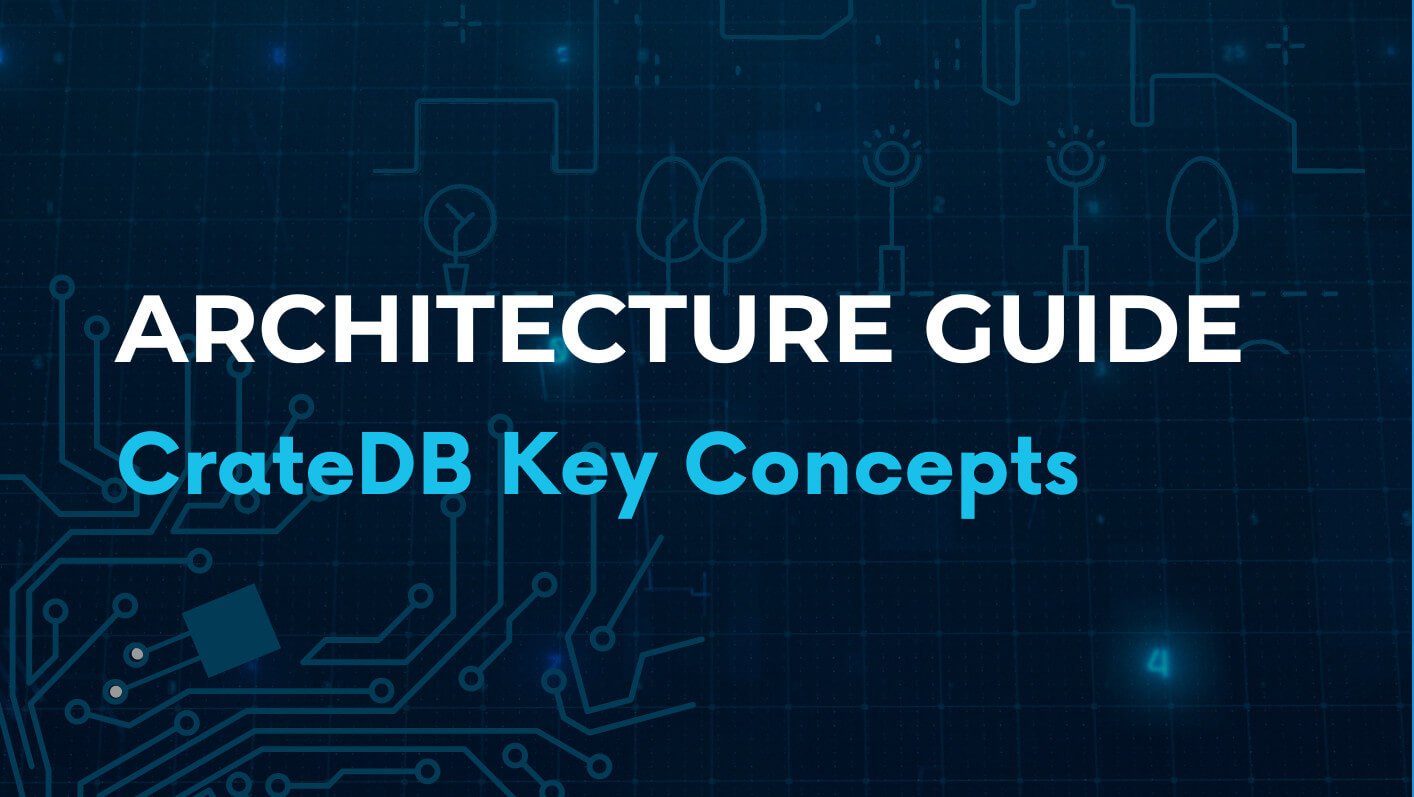
Horizontal Scalability
CrateDB is built for true horizontal scalability. As your data grows, your cluster grows with it, simply add nodes, and CrateDB automatically redistributes data and queries across them. No manual sharding, no reconfiguration, and no downtime. Just seamless, real-time scale-out performance that keeps pace with your business.
What horizontal scalability means
In a vertically scaled database, performance depends on a single machine, leading to more CPUs, more RAM, higher cost.
In a horizontally scaled database like CrateDB, performance grows by adding more nodes to the cluster.
Each new node brings its own compute, memory, and storage resources, allowing CrateDB to:
- Ingest and process millions of records per second
- Run complex analytical queries across billions of rows in milliseconds
- Scale linearly, without performance bottlenecks
This makes CrateDB ideal for IoT data streams, AI feature pipelines, and real-time analytics platforms that never stop growing.

How CrateDB achieves effortless scale-out
CrateDB’s scalability comes from its shared-nothing, distributed architecture: every node operates independently, yet collaborates as part of a unified SQL cluster.
When you add a new node:
- The cluster automatically recognizes it through node discovery.
- Shards (the physical units of data storage) are redistributed evenly.
- The query planner adapts instantly to include the new node in distributed queries.
- Data replication and balancing happen in the background, with zero downtime.
Your system capacity expands immediately, both in storage and processing power.
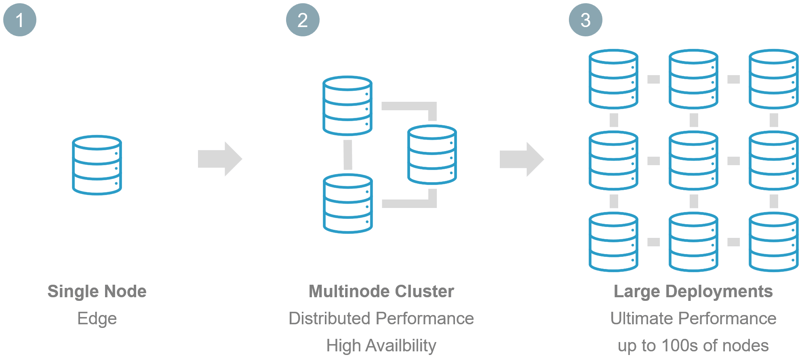
The diagram below illustrates the automatic redistribution process:
- The initial three node cluster utilizes about 70% of the available storage space.
- The addition of a new node results in an unbalanced distribution of data.
- The automatic redistribution of data initiates, until an almost equal level of storage consumption across the four nodes is achieved again.

Linear growth, predictable performance
- Each node processes queries in parallel on local data.
- The coordinator node merges intermediate results.
- Adding nodes means faster response times, not slower ones.

Built-in elasticity
- Elastic scaling: Add or remove nodes without interrupting queries.
- Rolling operations: Upgrades, maintenance, and rebalancing happen live.
- Consistent performance: Automatic load balancing keeps clusters evenly distributed.

Example: scaling out with a single command
ALTER CLUSTER ADD NODE '10.1.0.8';
In seconds, CrateDB redistributes shards, updates its execution plan, and starts routing queries through the new node:
no restarts, no reconfiguration, and no data movement downtime.
With CrateDB Cloud, you can even scale your infrastructure in just a few clicks:
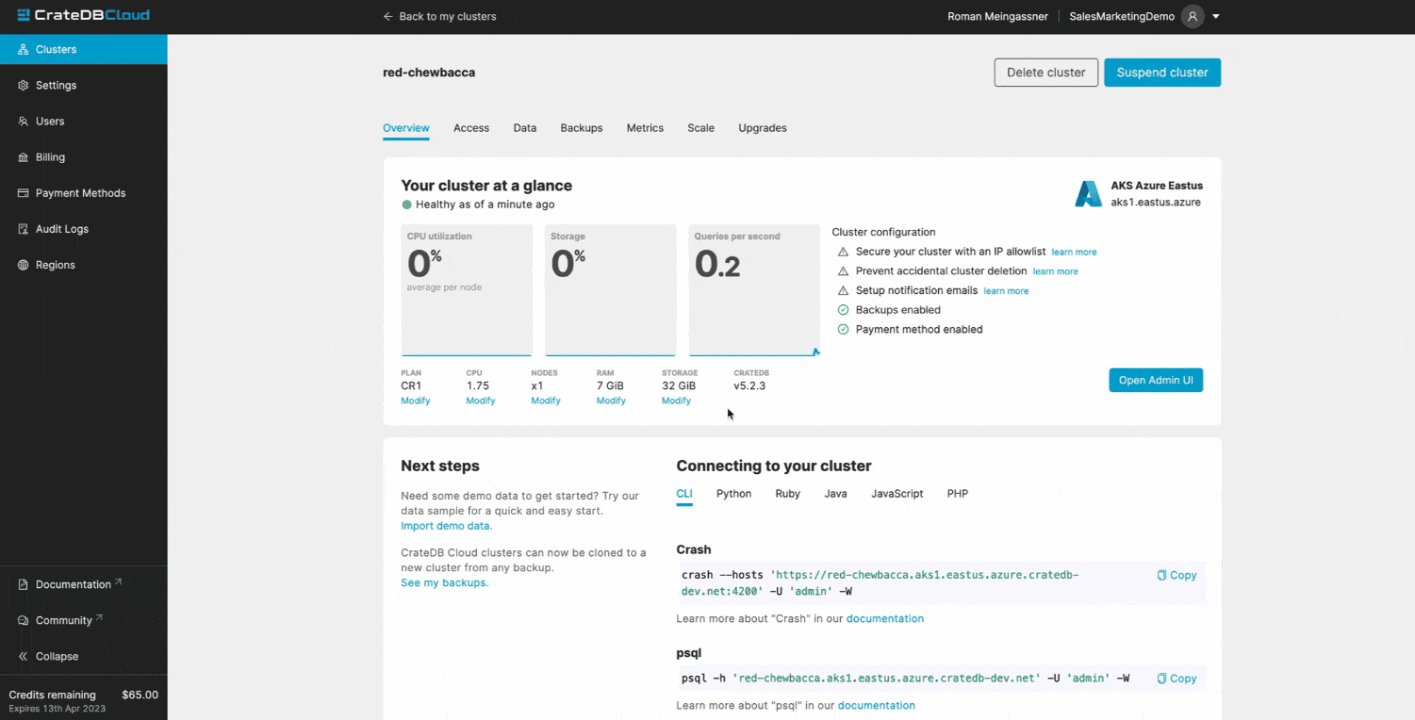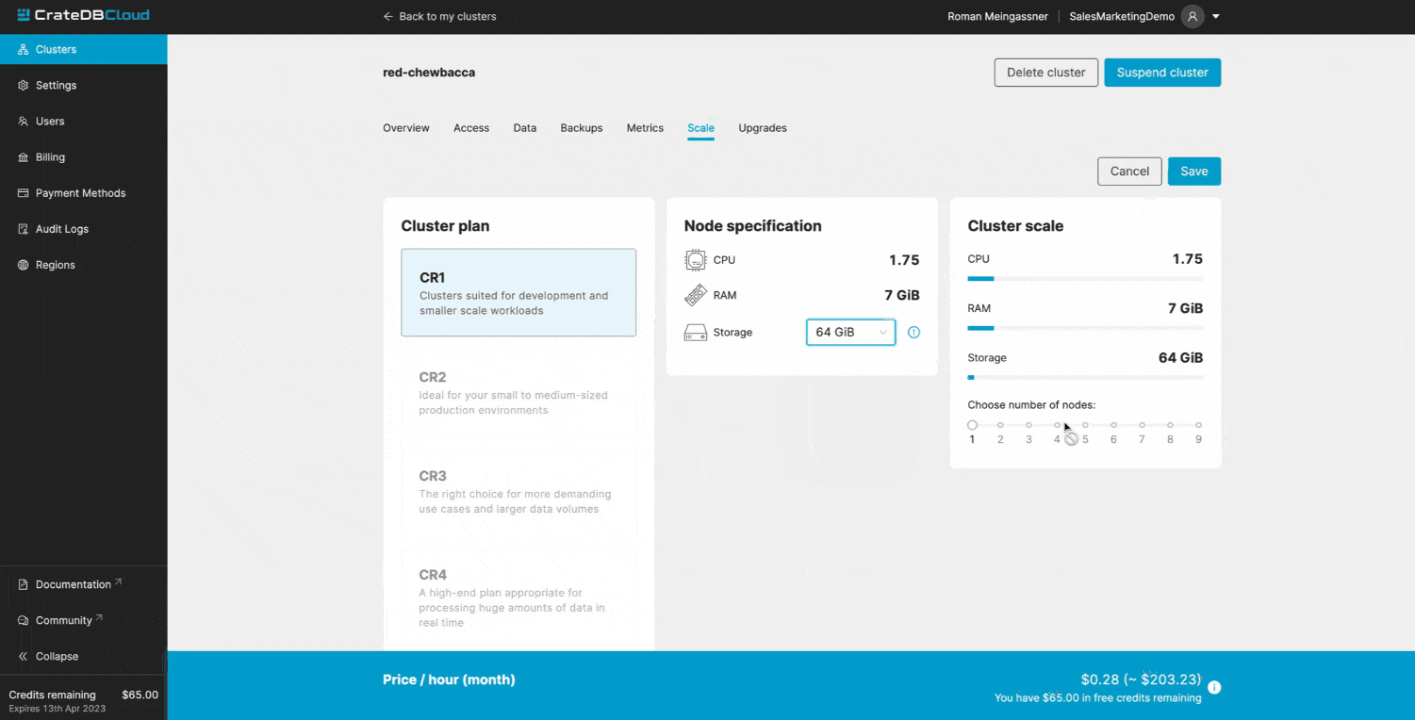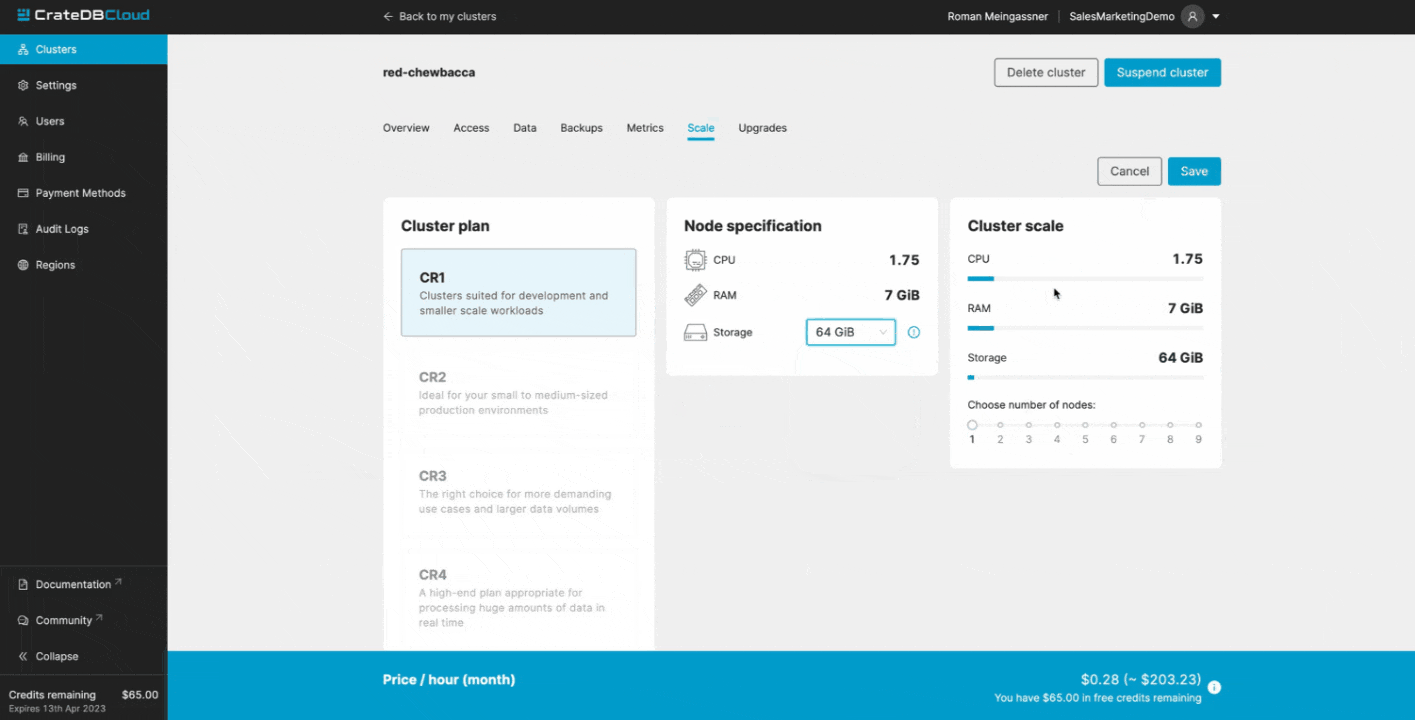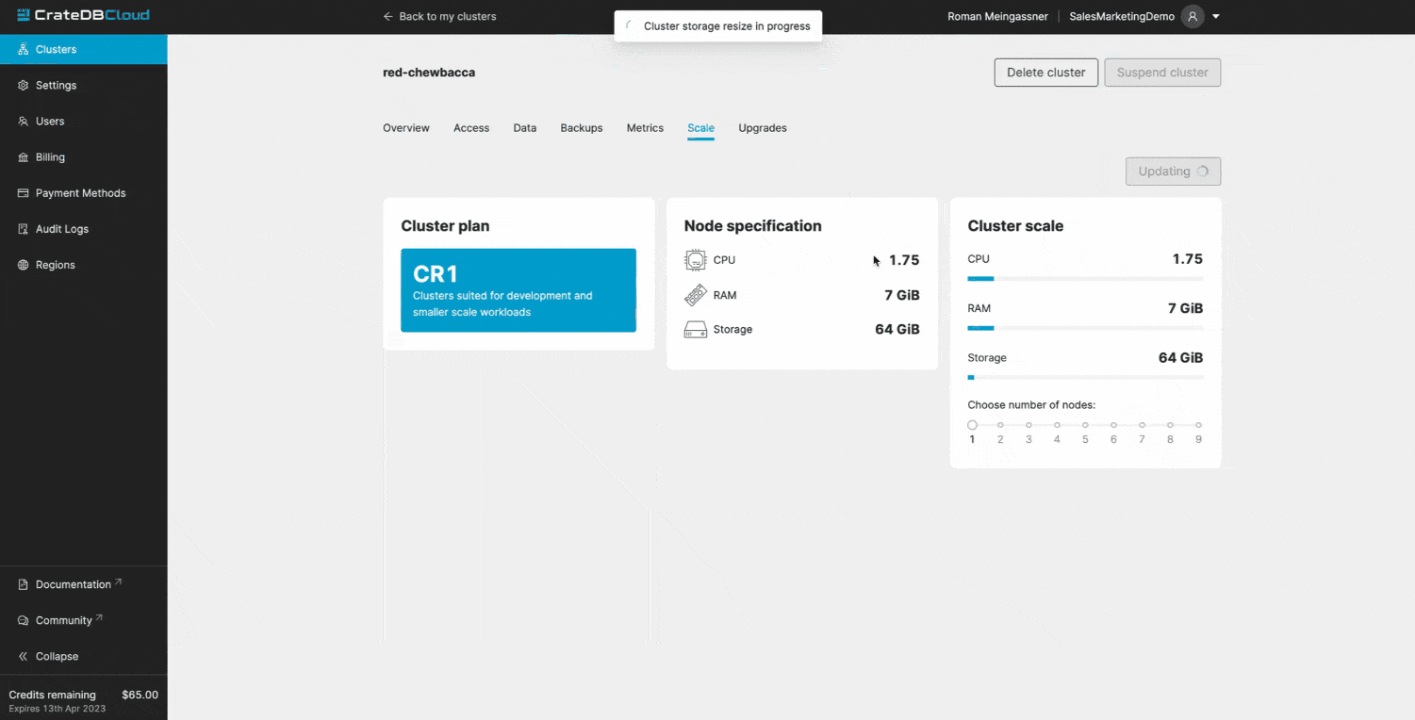

The benefits of horizontal scalability
| Challenge | CrateDB solution |
|---|---|
| Growing data volumes | Add nodes seamlessly to increase capacity |
| Performance degradation under load | Linear scaling of compute and storage resources |
| Downtime during maintenance | Rolling rebalancing and live updates |
| Complex sharding logic | Automatic data distribution and replication |
| Unpredictable workloads | Elastic scale-out and scale-in flexibility |

Scalable across any data type
CrateDB’s horizontal scalability applies to all data models, not just structured tables.
The distributed SQL engine scales out uniformly for:
- Time series data from sensors and devices
- Text and document search using MATCH
- Vector similarity queries for AI and semantic search
- JSON and nested objects
- Geospatial and location-based analytics

Why teams choose CrateDB for scale
- Start small, grow endlessly: Begin with a few nodes, scale to hundreds.
- No special configuration: Every node is equal; no primary/secondary setup.
- Predictable costs: Scale compute and storage independently, as needed.
- Future-proof: Designed for modern data growth, from IoT to AI.

CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.