Columnar Database: Definition, Architecture, and Use Cases
A columnar database, also known as a column-oriented database, is a database system that stores data by column rather than by row. This storage model is optimized for analytical workloads, where queries typically scan large volumes of data but access only a subset of columns. By reading only the relevant columns, columnar databases can process aggregations, filters, and analytical queries much more efficiently than traditional row-based databases.
Columnar databases are widely used in analytics, business intelligence, and data-intensive applications where performance, scalability, and fast query execution matter more than frequent single-row updates.
This page explains what a columnar database is, how it works, how it compares to row-based databases, and where it fits in modern data architectures.
What Is a Columnar Database?
In a columnar database, data is stored column by column instead of row by row.
In a traditional row-based database, all values for a single record are stored together. In a columnar database, all values for a single column are stored together across many rows. This difference fundamentally changes how data is read, compressed, and processed during queries.
Analytical queries often scan many rows, read only a few columns, and perform aggregations such as SUM, COUNT, or AVG. In this context, columnar storage significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be read from disk or memory.

How Columnar Storage Works
Consider a table storing sensor measurements: device_id, timestamp, temperature, humidity.
In a columnar database, each column is stored separately:
-
device_id values stored together
-
timestamp values stored together
-
temperature values stored together
-
humidity values stored together
When a query asks for the average temperature over time, the database can read only the temperature and timestamp columns, instead of scanning full rows that include unrelated fields.
This column-oriented storage layout enables:
-
faster sequential reads
-
better CPU cache utilization
-
efficient vectorized execution
-
strong data compression

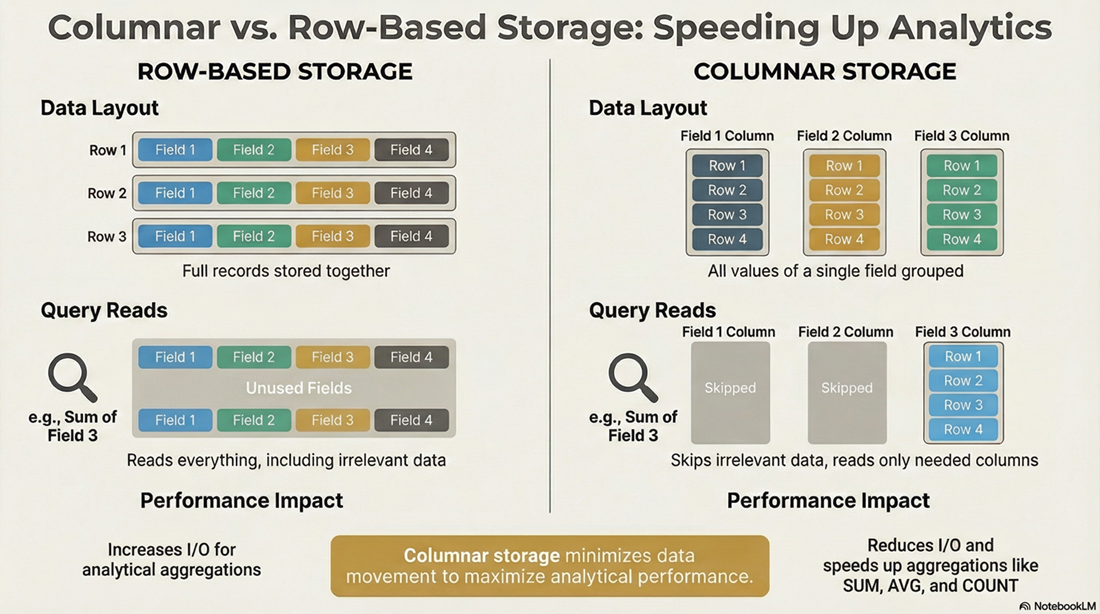
Columnar vs Row-Based Databases
The main difference between columnar and row-based databases lies in how they optimize for different workloads.
| Feature | Columnar Database | Row-Based Database |
|---|---|---|
| Storage layout | Column-oriented | Row-oriented |
| Best for | Analytics and aggregations | Transactions and point lookups |
| Read pattern | Many rows, few columns | Few rows, many columns |
| Compression | Very effective | Limited |
| Update frequency | Lower | Higher |
| Typical use cases | BI, dashboards, analytics | OLTP, CRUD applications |
Row-based databases excel at transactional workloads where individual records are frequently inserted, updated, or retrieved. Columnar databases excel at analytical workloads where large datasets are scanned and aggregated.

Why Columnar Databases Are Fast for Analytics
Columnar databases achieve high analytical performance through several key mechanisms.
Reduced I/O: Queries read only the columns they need, dramatically reducing disk and memory I/O.
Compression: Columns often contain similar values, enabling high compression ratios that reduce storage and speed up scans.
Vectorized Execution: Many columnar engines process data in batches, applying operations to vectors of values rather than one row at a time.
Efficient Aggregations: Operations like GROUP BY, COUNT, and SUM are optimized when data is stored column-wise.
Together, these characteristics make columnar databases well suited for large-scale analytical queries.

Trade-Offs and Limitations
While columnar databases are powerful, they are not ideal for every workload.
Common limitations include:
-
Slower performance for frequent single-row inserts or updates
-
Higher complexity for mixed transactional and analytical workloads
-
Increased write amplification if data must be reorganized into columnar format
For these reasons, columnar databases are often used alongside transactional systems rather than replacing them entirely.

Common Use Cases for Columnar Databases
Columnar databases are commonly used in scenarios such as:
-
Analytical dashboards and reporting
-
Time-series and event data analysis
-
Log and telemetry analytics
-
Business intelligence platforms
-
Monitoring and observability systems
-
Large-scale aggregations across high-cardinality data
These use cases share a common requirement: fast analytical queries over large volumes of data.

Examples of Columnar Databases
Many modern analytics systems use columnar storage, including:
-
Analytical data warehouses: Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse Analytics
-
OLAP databases: ClickHouse, Apache Druid, Apache Pinot, MonetDB
-
Distributed analytics engines: Apache Spark, Presto, Trino, Apache Impala
-
Real-time analytics platforms: CrateDB, Apache Druid, Apache Pinot
Some systems focus on batch analytics over historical data, while others extend columnar storage to support real-time ingestion and querying.

Columnar Databases in Modern Data Architectures
In modern data stacks, columnar databases typically sit between data ingestion pipelines and analytics or application layers.
They may:
-
ingest data from streams, logs, or applications
-
store both historical and recent data
-
serve analytical queries directly to dashboards or APIs
As analytics moves closer to operational systems, some columnar databases are designed to handle continuously arriving data while still delivering fast query performance.

Columnar Storage in CrateDB
Unlike traditional analytical systems that rely on batch loading or pre-aggregation, CrateDB is designed to ingest data continuously while keeping it immediately queryable. This makes columnar storage usable not only for historical analysis but also for operational and real-time analytics use cases.
By combining columnar storage with distributed query execution and SQL access, CrateDB enables teams to run analytical queries on fresh and historical data in the same system.

When to Use a Columnar Database
A columnar database is a strong choice when:
-
queries scan large datasets
-
analytics and aggregations are the primary workload
-
performance matters more than frequent row-level updates
-
data volumes grow quickly over time
Understanding these trade-offs helps determine whether a columnar database fits your use case and where it belongs in your overall data architecture.

Additional resources
FAQ
A columnar database is a database system that stores data by column rather than by row, optimizing analytical queries that scan large datasets.
Columnar databases store data by column and are optimized for analytics, while row-based databases store data by row and are optimized for transactional workloads and point lookups.
A columnar database is best suited for analytical workloads that involve scanning large volumes of data, running aggregations, and analyzing trends across many rows and dimensions.
Some columnar databases support real-time analytics, but performance depends on how well the system handles continuous ingestion and query execution on fresh data.