Replication
CrateDB ensures continuous availability and data protection through replication, a mechanism that maintains multiple copies of your data across nodes within a cluster.
By replicating data at the shard level, CrateDB guarantees that your data remains available even when nodes fail or go offline for maintenance.
Each shard has one or more replica shards, which automatically take over if the primary shard becomes unavailable.
This design not only enhances fault tolerance but also boosts query performance, since read operations can be distributed across multiple replicas.

How replication works
In CrateDB, data replication happens automatically as part of the cluster’s distributed storage system:
- Shard-level replication: Each table’s data is divided into shards, and each shard has one or more replicas stored on different nodes.
- Automatic failover: If a node fails or a primary shard becomes unavailable, CrateDB automatically promotes one of its replicas to primary status, ensuring uninterrupted access.
- Real-time synchronization: Updates to primary shards are synchronously written to all active replicas to maintain consistency across nodes.
- Optimized recovery: When nodes rejoin the cluster, CrateDB efficiently synchronizes only missing or changed data using Lucene’s append-only storage model.

Performance and scalability
Replication in CrateDB not only protects your data, it also improves performance.
- Parallel read execution: Read queries are executed across primary and replica shards simultaneously, distributing workload across the cluster and accelerating response times.
- Load balancing: CrateDB randomly assigns shards for read operations by default, preventing hotspots and ensuring balanced resource utilization.
- Configurable behavior: Administrators can fine-tune replication settings to optimize for redundancy, latency, or throughput based on their environment.

Relationship with sharding and partitioning
Replication complements sharding and partitioning to provide full scalability and fault tolerance:
- Sharding splits data into parallel units for distributed processing.
- Partitioning organizes large datasets logically (e.g., by time).
- Replication ensures every shard has redundant copies for availability and faster reads.

Benefits of replication
- High availability: Continuous uptime even during node failures or maintenance.
- Data protection: Automatic promotion of replica shards prevents data loss.
- Faster queries: Read operations can be served from any replica, improving cluster-wide throughput.
- Load distribution: Query load is balanced evenly across all available nodes.
- Synchronous consistency: Writes are replicated in real time to ensure accuracy and reliability.

Best practices
- Maintain at least two replicas (primary + secondary) for production workloads.
- Distribute replicas across different nodes, racks, or availability zones to minimize correlated failure risk.
- Monitor replication lag and resource utilization to ensure optimal sync performance.
- Combine replication with incremental backups for comprehensive disaster recovery.

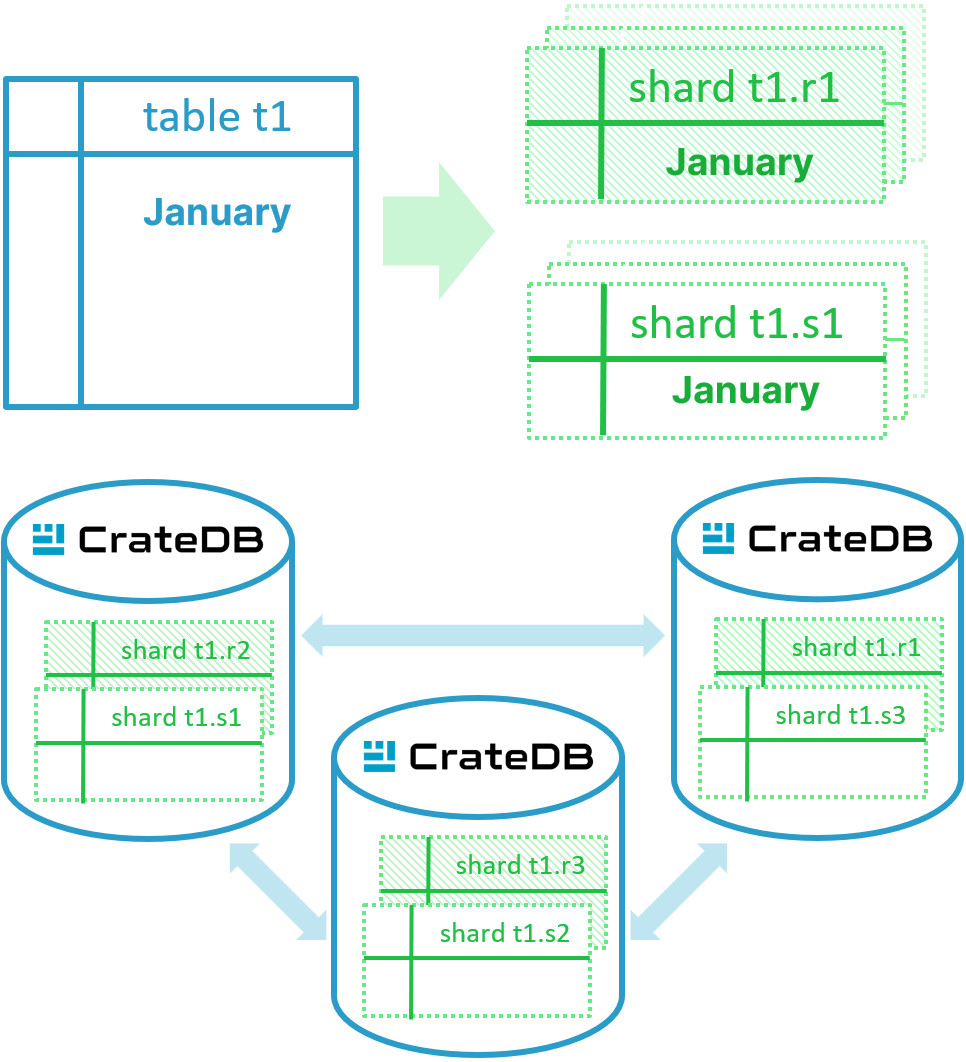
CREATE TABLE t1 ( name STRING ) CLUSTERED INTO 3 SHARDS WITH (“number_of_replicas” = '1');
CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.