In one of our previous blog posts, we explained how to apply Change Data Capture (CDC) from DynamoDB to CrateDB. In that example, DynamoDB integrates natively with Kinesis, but we need a more generic approach to unlock support for other DBMS, such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, or SQL Server.
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
DMS is a managed AWS service that enables one-time and continuous replications. Our use case is an ongoing replication of changes from upstream database systems into CrateDB. DMS will help us capture CDC events from various source endpoints and translate them into a common format which we can finally translate into standard SQL.

Relational databases are well-suited for applications requiring structured data management, ACID transactions, and strong data integrity, such as financial systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications. CrateDB, on the other hand, is a highly scalable distributed database that excels in handling both structured and semi-structured data, making it ideal for real-time analytics and (hybrid) search applications. Rapid access and performance over a multitude of data types like time series, nested JSONs, geospatial, full-text search, and similarity search are critical in such scenarios. By implementing Change Data Capture (CDC) to move data from relational databases into CrateDB, organizations can leverage the strengths of both systems. This approach solves scalability issues and enhances the ability to perform complex queries on large datasets without compromising performance, enabling comprehensive data analysis and integration across diverse data types.
Example
In our example, we look at capturing climate data, which splits into two entities:
-
locations(stored in PostgreSQL): Master data on locations from which measurements are taken -
conditions(stored in CrateDB): High-frequency time-series data with readings submitted by sensors
Setup
In PostgreSQL, we create our locations table. The JSONB data type is used to store dynamic attributes that might not be present for every location.
CREATE TABLE public.locations ( device_id TEXT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, location TEXT, attributes JSONB );
In CrateDB, we create a matching target table. We leave it intentionally generic using CrateDB’s OBJECT(DYNAMIC) and leave it to the replication process to dynamically evolve the schema:
CREATE TABLE locations (data OBJECT(DYNAMIC));
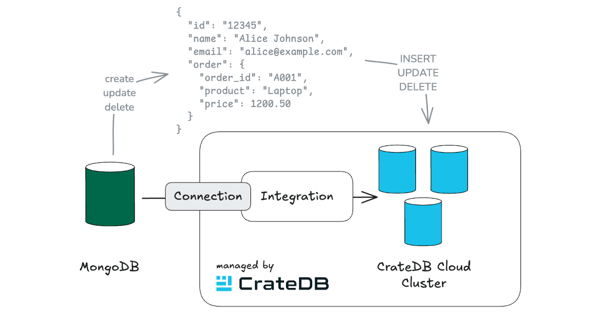
There are various options on how to set up DMS itself. We focus here on key aspects that are relevant to the translation of CDC events. This results in the architecture below:

Our PostgreSQL server acts as a source endpoint, and DMS pushes standardized CDC events to a sink endpoint, which is a Kinesis stream. The stream gets consumed by a Lambda function. Using a Lambda function provides flexibility to inject additional logic to perform any data cleansing or data transformation tasks. Below you can find a simplified version of the Lambda implementation which illustrates the main workflow. The full version can be found on GitHub.
import base64 import json import os import sqlalchemy as sa from commons_codec.model import ColumnTypeMapStore from commons_codec.transform.aws_dms import DMSTranslatorCrateDB # Input on type mappings, e.g. for JSON/OBJECT columns COLUMN_TYPES: str = os.environ.get("COLUMN_TYPES", "") # Connection information for CrateDB CRATEDB_SQLALCHEMY_URL: str = os.environ.get("SINK_SQLALCHEMY_URL", "crate://") column_types = ColumnTypeMapStore.from_json(COLUMN_TYPES) # The translator translates from DMS CDC to SQL cdc = DMSTranslatorCrateDB(column_types=column_types # Connect to CrateDB engine = sa.create_engine(CRATEDB_SQLALCHEMY_URL) connection = engine.connect() def handler(event, _context): for record in event["Records"]: event_id = record["eventID"] try: # Decode the serialized CDC event record_data = json.loads(base64.b64decode(record["kinesis"]["data"]).decode("utf-8")) # Translate from CDC to SQL sql = cdc.to_sql(record_data) # Execute the SQL statement connection.execute(sa.text(sql)) connection.commit() except UnknownOperationError as ex: logger.warning(f"Ignoring message. Reason: {ex}. Record: {ex.record}") except Exception as ex: error_message = f"An error occurred processing event: {event_id}" logger.exception(error_message) logger.info(f"Successfully processed {len(event['Records'])} records")
Matching data types
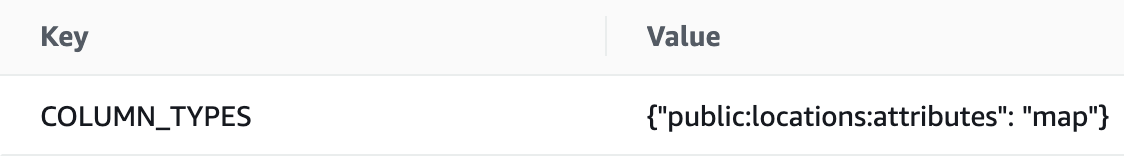
DMS needs to map a source system’s data types to a generic set of shared data types. A mapping is available for each DBMS, such as PostgreSQL. Mapping primitive data types is straightforward, but JSONB gets mapped to NCLOB. Even though JSON documents can be serialized as strings, we lose data type information. To compensate for that, we parametrize the Lambda function with a type mapping.
For our locations source table, we specify the fully qualified name of the JSONB attributes column and set the value to map. It makes the Lambda function unwrap the JSON document and allows CrateDB to recognize it as a JSON structure.
Let’s try it
We start by populating the source tables with data:
INSERT INTO locations VALUES ('weather-pro-000054', 'arctic-000013', '{"environment": "outside", "active": true, "firmware_version": 2}' ('weather-pro-000715', 'door-00078', '{"environment": "doorway", "active": false, "firmware_version": 2}'), ('weather-pro-000094', 'swamp-000017', '{"environment": "outside", "active": false, "firmware_version": 2}');
Any DML statement is supported, such as updates:
UPDATE locations SET attributes['active'] = TO_JSONB(true) WHERE device_id = 'weather-pro-000715';
We can also add a new JSON attribute as well:
UPDATE locations SET attributes['last_updated'] = TO_JSONB(NOW());

Finally, we can now join our replicated tables with already existing time-series data and create a report that combines columns:

Summary
AWS Database Migration Service takes away a lot of complexity by dealing with different CDC formats. To integrate with CrateDB, we translate those to SQL and execute CDC events in real time. Even though additional type mapping can be needed to compensate for data type generalization, the general process of translating CDC events works with minimal effort.
Do you want to replicate data from your DBMS into CrateDB? Contact us and we will gladly assist with setting up a customized replication process for you.