Distributed Database Architecture
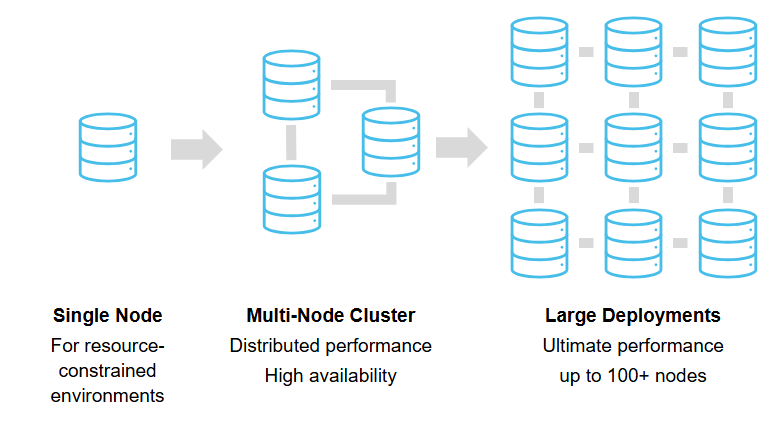
CrateDB is built as a distributed database using a shared-nothing architecture designed for real-time analytics on large, fast-moving datasets. Instead of relying on a single node, CrateDB distributes data storage, ingestion, and query execution across a cluster, allowing it to scale horizontally while remaining resilient to failures.
If you are looking for a general definition of distributed databases and common architectures, see our distributed database overview.
Built for modern data demands
Traditional databases were never designed for the scale of billions of events, streaming data, diverse formats, and real-time decision making.
CrateDB’s distributed architecture breaks through these limits by spreading both data and query execution across multiple nodes. Each node works independently, processing its share of the workload in parallel.
- Linear scalability: Add nodes to handle more data or queries instantly.
- High throughput: Ingest millions of events per second with consistent performance.
- Distributed execution: Queries are automatically parallelized across all nodes for millisecond-level results.
- Resilient by design: Built-in replication and failover ensure continuous availability.

How CrateDB distributes work
- Data sharding: Tables are automatically partitioned into shards distributed across nodes.
- Replication: Each shard is replicated to multiple nodes to prevent data loss.
- Query distribution: The distributed SQL engine sends query tasks to the nodes holding relevant data.
- Parallel processing: Each node processes its part locally and returns intermediate results.
- Result aggregation: The handler node merges results and returns the final output in milliseconds.
- Everything happens automatically: no manual sharding, no complex clustering setup, no downtime.

Multi-model and real-time
CrateDB’s distributed engine isn’t limited to relational data. It processes time series, text, JSON, geospatial, and vector data, all in real time.
Whether you’re monitoring sensors, searching documents, or serving AI models, CrateDB delivers the same speed, scale, and simplicity across every data type.

Enterprise-grade reliability
- Automatic failover: Continuous operation, even if nodes fail.
- Self-healing clusters: Nodes rejoin and resynchronize automatically.
- Rolling upgrades: Apply maintenance without downtime.
- Multi-zone deployments: Distribute nodes across regions for resilience.
This high availability makes CrateDB a natural fit for mission-critical analytics, IoT platforms, and AI-driven applications.

CrateDB architecture guide
This comprehensive guide covers all the key concepts you need to know about CrateDB's architecture. It will help you gain a deeper understanding of what makes it performant, scalable, flexible and easy to use. Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about when to leverage CrateDB for your data projects.
Additional resources
Want to learn more?
FAQ
CrateDB is built using a shared-nothing distributed architecture. Data storage, ingestion, and query execution are distributed across multiple nodes in a cluster, allowing the system to scale horizontally and operate without a central bottleneck.
Data is replicated across multiple nodes to ensure availability and durability. If a node fails, replicas allow queries and ingestion to continue without interruption while the system automatically recovers and rebalances data.
Queries are planned and executed in parallel across nodes. Each node processes the data it owns locally, and partial results are combined to produce the final query result. This distributed execution model enables fast analytical queries on large datasets.
CrateDB supports continuous ingestion with near real-time indexing, allowing newly ingested data to be queried almost immediately. This makes it suitable for real-time analytics workloads that require fresh data without batch processing or pre-aggregation.
Yes. Nodes can be added to a running cluster to increase storage and compute capacity. CrateDB automatically redistributes data and balances load across the cluster without requiring manual shard management or downtime.
CrateDB is optimized for analytical workloads on large and fast-moving datasets. Its distributed architecture is designed for high ingestion rates, aggregations, and analytical queries rather than high-volume transactional workloads.
Traditional databases typically run on a single node and scale vertically. CrateDB’s distributed architecture scales horizontally, distributes both data and queries, and provides built-in resilience, making it better suited for large-scale and real-time analytics use cases.
For a general overview of distributed databases, architectures, and use cases, see our distributed database overview page.