Streaming & Real-Time Analytics
CrateDB ingests and analyzes continuously arriving data as it is generated. It enables sub-second queries on fresh events and time-series data, allowing teams to build dashboards, alerts, and applications that reflect what is happening right now, not minutes or hours later.
Modern systems produce constant streams of data from connected devices, sensors, machines, vehicles, applications, and infrastructure logs. Turning this flow of events into timely insight requires more than storage at scale. It requires the ability to ingest data continuously and query it immediately, without batch windows or pre-computed aggregates.
Streaming and real-time analytics enable teams to monitor live systems, detect anomalies as they occur, and act on current conditions with confidence.
Continuous Ingestion at Scale
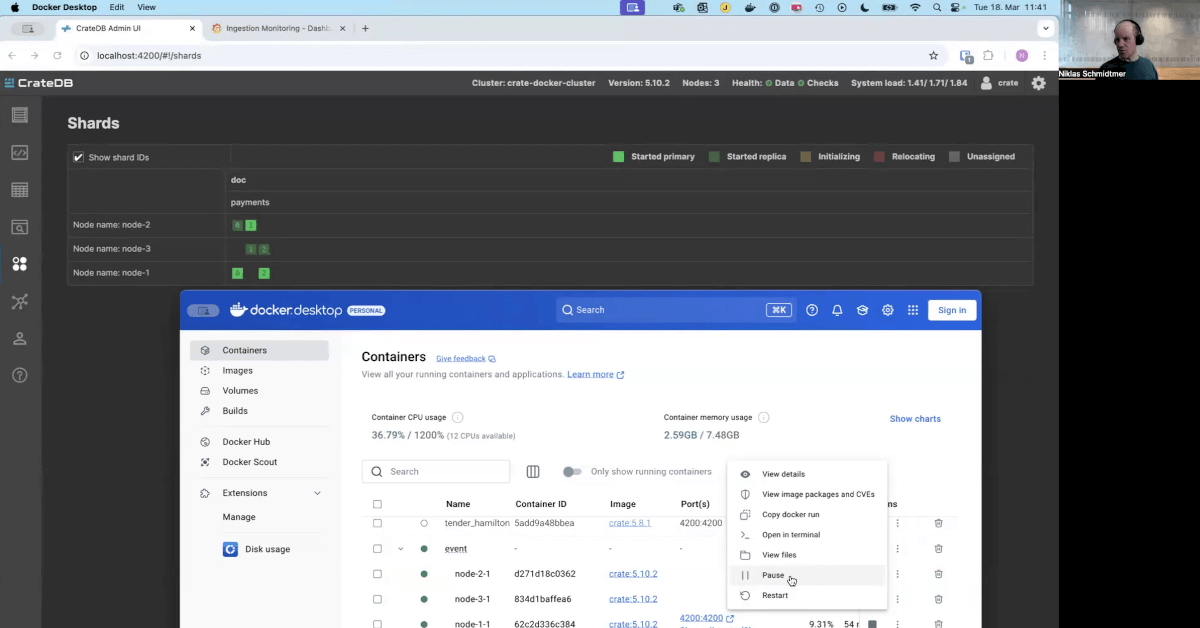
CrateDB ingests high-velocity data streams from sources such as Kafka, Flink, MQTT, and CDC pipelines. Data is distributed across the cluster as it arrives, enabling sustained ingestion rates without bottlenecks or manual tuning.

Query Fresh Data Instantly
New events become queryable within milliseconds. Teams can run analytical queries on live data streams without waiting for batch jobs, pre-aggregation, or indexing delays, making fresh data immediately usable.

Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
CrateDB powers live dashboards and alerting systems that reflect the current state of operations. This enables immediate detection of anomalies and rapid response to changes in system behavior or business conditions.

Built for Always-On Workloads

Where Traditional Systems Fall Short
Traditional databases and data warehouses struggle with continuous streams of events:
- Time lag: Data must often be pre-aggregated or batch-processed, delaying insights.
- Scale limits: Billions of events overwhelm OLTP databases like Postgres or MongoDB.
- High cost: Warehouses become expensive at high ingestion rates and are not designed for low-latency queries on fresh data.
As a result, organizations miss anomalies, react too late to operational issues, and struggle to power real-time dashboards or downstream AI systems effectively.

Is CrateDB the Right Database for Your Workloads?
Answer 10 questions. Get your score. No email required.
Sensor data queries with SQL
Hyper-fast. Results in milliseconds.
/* Based on IoT devices reports, this query returns the voltage variation over time
for a given meter_id */
WITH avg_voltage_all AS (
SELECT meter_id,
avg("Voltage") AS avg_voltage,
date_bin('1 hour'::INTERVAL, ts, 0) AS time
FROM iot.power_consumption
WHERE meter_id = '840072572S'
GROUP BY 1, 3
ORDER BY 3
)
SELECT time,
(avg_voltage - lag(avg_voltage) over (PARTITION BY meter_id ORDER BY time)) AS var_voltage
FROM avg_voltage_all
LIMIT 10;
+---------------+-----------------------+
| time | var_voltage |
+---------------+-----------------------+
| 1166338800000 | NULL |
| 1166479200000 | -2.30999755859375 |
| 1166529600000 | 4.17999267578125 |
| 1166576400000 | -0.3699951171875 |
| 1166734800000 | -3.7100067138671875 |
| 1166785200000 | -1.5399932861328125 |
| 1166893200000 | -3.839996337890625 |
| 1166997600000 | 9.25 |
| 1167044400000 | 0.4499969482421875 |
| 1167174000000 | 3.220001220703125 |
+---------------+-----------------------+
/* Based on IoT devices reports, this query returns the voltage corresponding to
the maximum global active power for each meter_id */
SELECT meter_id,
max_by("Voltage", "Global_active_power") AS voltage_max_global_power
FROM iot.power_consumption
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC
LIMIT 10;
+------------+--------------------------+
| meter_id | voltage_max_global_power |
+------------+--------------------------+
| 840070437W | 246.77 |
| 840073628P | 246.69 |
| 840074265G | 246.54 |
| 840070238E | 246.35 |
| 840070335K | 246.34 |
| 840075190M | 245.15 |
| 840072876X | 244.81 |
| 840070636M | 242.98 |
| 84007B113A | 242.93 |
| 840073250D | 242.28 |
+------------+--------------------------+
Want to know more?
User stories

"It is through the use of CrateDB that we are able to offer our large-scale video analytics component in the first place. Comparable products are either not capable of handling the large flood of data or they are simply too expensive."
Daniel Hölbling-Inzko
Senior Director of Engineering - Analytics
Bitmovin


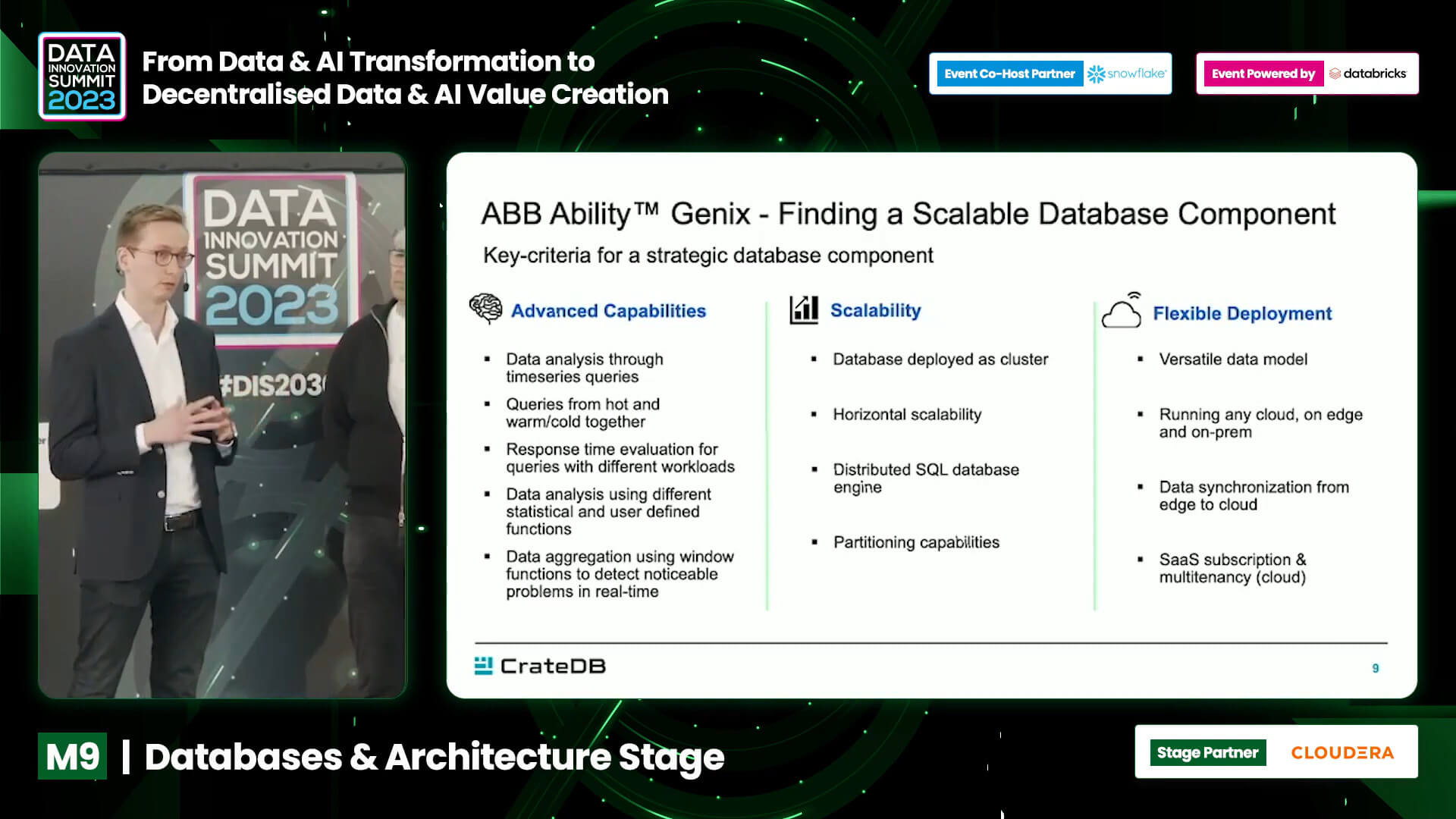
ABB's OPTIMAX® Cloud for Smart Charging is a state-of-the-art power management system designed for EV charging stations and heavy vehicle depots in the logistics and bus industries. It provides smart load management for ABB and non ABB EV chargers, and integrates with external assets like battery storages, PV systems, and interfaces to grid operators’ systems.
"CrateDB is a critical piece of our OPTIMAX® Cloud platform. Its ability to handle vast amounts of time-series data from diverse sources, while delivering real-time insights, has allowed us to scale our operations seamlessly. With CrateDB, we’ve empowered our customers with smarter energy management, reduced costs, and supported a more sustainable future."
Christian Kohlmeyer
Product Owner Mobility & Sites
ABB


Using CrateDB, TGW accelerates data aggregation and access from warehouse systems worldwide, resulting in increased database performance. The system can handle over 100,000 messages every few seconds.
"CrateDB is a highly scalable database for time series and event data with a very fast query engine using standard SQL".
Alexander Mann
Owner Connected Warehouse Architecture
TGW Logistics Group


"With CrateDB, we can continue designing products that add value to our customers. We will continue to rely on CrateDB when we need a database that offers great scalability, reliability and speed."
Nixon Monge Calle
Head of IT Development and Projects
SPGo! Business Intelligence


"CrateDB is the only database that gives us the speed, scalability and ease of use to collect and aggregate measurements from hundreds of thousands of industrial sensors for real-time visibility into power, temperature, pressure, speed and torque."
Jürgen Sutterlüti
Vice President, Energy Segment and Marketing at Gantner Instruments.
Additional resources
FAQ
Streaming analytics refers to real-time processing and analysis of data as it flows in (e.g. from sensors, logs, events). It allows organizations to detect anomalies, trigger actions, and make decisions immediately, rather than relying on batch processing that introduces latency.
CrateDB is engineered for scalable ingestion from sources such as Kafka, MQTT, CDC streams, and logs. It features automatic indexing and distributed architecture that let it scale horizontally and sustain large throughput while serving sub-second queries.
Yes, CrateDB supports native SQL. You can query streaming and time-series data using familiar SQL semantics (aggregations, windowing, joins) without needing to learn a proprietary query language.
CrateDB supports flexible schemas, allowing you to ingest semi-structured data (e.g. JSON fields) and evolve your schema over time. This makes it easier to adapt as new sources and fields emerge.
It’s particularly effective in scenarios such as IoT (sensor monitoring), log and event analytics, anomaly detection, fleet/transport monitoring, real-time dashboards, AI/ML feature pipelines, and any system requiring near-instant insight from high-volume continuous data.